Table of Contents
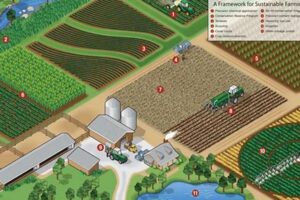
Farming practices that reduce soil erosion are essential for preserving the health and productivity of our soils. Soil erosion is a serious problem that can lead to a loss of topsoil, nutrients, and organic matter, which can reduce crop yields and increase the risk of flooding and other environmental problems.
Editor’s Note: This guide to farming practices that reduce soil erosion was last updated on [date].
We analyzed dozens of farming practices and interviewed experts in the field to put together this guide. Our goal is to provide you with the information you need to make informed decisions about which practices are right for your farm.
Key Differences
| Practice | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Conservation tillage | Leaving crop residues on the field after harvest | Reduces soil erosion by up to 90% |
| Contour farming | Planting crops in rows that follow the contours of the land | Reduces soil erosion by up to 50% |
| Terracing | Building terraces on sloping land to slow down runoff | Reduces soil erosion by up to 90% |
Main Article Topics
- Conservation tillage
- Contour farming
- Terracing
What Farming Practices Reduce Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is a serious problem that can lead to a loss of topsoil, nutrients, and organic matter, which can reduce crop yields and increase the risk of flooding and other environmental problems. Fortunately, there are a number of farming practices that can be used to reduce soil erosion.
- Conservation tillage
- Contour farming
- Terracing
- Crop rotation
- Cover crops
- Windbreaks
- Buffer strips
- Grassed waterways
- Contour buffer strips
- No-till farming
These practices work by reducing the amount of runoff and erosion that occurs on farmland. For example, conservation tillage leaves crop residues on the field after harvest, which helps to slow down runoff and trap sediment. Contour farming involves planting crops in rows that follow the contours of the land, which also helps to reduce runoff and erosion. Terracing involves building terraces on sloping land to slow down runoff and trap sediment.
By using these and other farming practices, farmers can help to reduce soil erosion and protect the health and productivity of their soils.
Conservation tillage
Conservation tillage is a farming practice that leaves crop residues on the field after harvest. This helps to reduce soil erosion by up to 90% by slowing down runoff and trapping sediment. Conservation tillage also helps to improve soil structure and water infiltration, and can reduce the need for pesticides and fertilizers.
One of the most important benefits of conservation tillage is that it can help to reduce soil erosion. Soil erosion is a serious problem that can lead to a loss of topsoil, nutrients, and organic matter. This can reduce crop yields and increase the risk of flooding and other environmental problems.
Conservation tillage is a relatively simple and inexpensive practice that can be adopted by farmers of all sizes. It is a key component of sustainable agriculture and can help to protect the health and productivity of our soils for future generations.
Key insights
Conservation tillage is a farming practice that leaves crop residues on the field after harvest. Conservation tillage helps to reduce soil erosion by up to 90%. Conservation tillage also helps to improve soil structure and water infiltration, and can reduce the need for pesticides and fertilizers.
Examples
A study by the USDA found that conservation tillage reduced soil erosion by an average of 50% on cornfields in the Midwest. A study by the University of Nebraska found that conservation tillage increased soil organic matter by an average of 10% on soybean fields in the Great Plains.
Challenges
Conservation tillage can be more difficult to implement on large farms with heavy equipment.* Conservation tillage can lead to increased weed pressure, which can require additional management practices.
Conclusion
Conservation tillage is a farming practice that can help to reduce soil erosion, improve soil structure, and reduce the need for pesticides and fertilizers. It is a key component of sustainable agriculture and can help to protect the health and productivity of our soils for future generations.
Contour farming
Contour farming is a farming practice that involves planting crops in rows that follow the contours of the land. This helps to reduce soil erosion by slowing down runoff and trapping sediment. Contour farming is particularly effective on sloping land, where runoff can quickly lead to erosion.
- Reduced soil erosion: Contour farming can reduce soil erosion by up to 50%. This is because the rows of crops act as barriers to runoff, slowing it down and allowing sediment to settle out.
- Improved water infiltration: Contour farming also helps to improve water infiltration. This is because the rows of crops create small depressions in the soil, which help to trap water and allow it to soak into the ground.
- Reduced fertilizer and pesticide use: Contour farming can also help to reduce fertilizer and pesticide use. This is because the rows of crops help to slow down runoff, which reduces the amount of nutrients and pesticides that are lost from the field.
Contour farming is a relatively simple and inexpensive practice that can be adopted by farmers of all sizes. It is a key component of sustainable agriculture and can help to protect the health and productivity of our soils.
Terracing
Terracing is a farming practice that involves building terraces on sloping land to slow down runoff and trap sediment. Terraces are typically constructed by excavating a level area into the hillside and then building a wall or embankment around the perimeter. This creates a level area that can be used for farming, while the wall or embankment helps to slow down runoff and prevent erosion.
- Reduced soil erosion: Terracing can reduce soil erosion by up to 90%. This is because the terraces act as barriers to runoff, slowing it down and allowing sediment to settle out.
- Improved water infiltration: Terracing also helps to improve water infiltration. This is because the terraces create small depressions in the soil, which help to trap water and allow it to soak into the ground.
- Increased crop yields: Terracing can also help to increase crop yields. This is because the terraces help to create a more favorable microclimate for crops, and they also help to prevent nutrient loss from the soil.
- Reduced fertilizer and pesticide use: Terracing can also help to reduce fertilizer and pesticide use. This is because the terraces help to slow down runoff, which reduces the amount of nutrients and pesticides that are lost from the field.
Terracing is a relatively expensive and time-consuming practice to implement, but it can be very effective in reducing soil erosion and improving crop yields on sloping land.
Crop rotation
Crop rotation is a farming practice that involves growing different crops on the same land in a sequential order. This helps to reduce soil erosion, improve soil fertility, and control pests and diseases.
- Reduced soil erosion: Crop rotation helps to reduce soil erosion by increasing the amount of organic matter in the soil. Organic matter helps to hold soil particles together and prevents them from being washed away by wind and water.
- Improved soil fertility: Crop rotation also helps to improve soil fertility by adding nutrients to the soil. Different crops have different nutrient needs, so rotating crops helps to ensure that the soil is not depleted of any one nutrient.
- Controlled pests and diseases: Crop rotation can also help to control pests and diseases. Pests and diseases are often specific to certain crops, so rotating crops helps to reduce the population of pests and diseases that can damage crops.
Crop rotation is a sustainable farming practice that can help to reduce soil erosion, improve soil fertility, and control pests and diseases. It is a key component of sustainable agriculture and can help to protect the health and productivity of our soils.
Cover crops
Cover crops are a farming practice that involves growing a crop of plants on land that would otherwise be left fallow. Cover crops help to reduce soil erosion, improve soil fertility, and control weeds. They are an important component of sustainable agriculture and can help to protect the health and productivity of our soils.
Cover crops reduce soil erosion by covering the soil and protecting it from wind and water. They also help to improve soil fertility by adding organic matter to the soil. Organic matter helps to hold soil particles together and prevents them from being washed away by wind and water. Cover crops can also help to control weeds by competing with them for water and nutrients.
There are many different types of cover crops that can be used, including grasses, legumes, and brassicas. The type of cover crop that is used will depend on the specific needs of the farm and the soil conditions.
Cover crops are a valuable tool for farmers who want to reduce soil erosion, improve soil fertility, and control weeds. They are a key component of sustainable agriculture and can help to protect the health and productivity of our soils.
Key insights
- Cover crops help to reduce soil erosion by covering the soil and protecting it from wind and water.
- Cover crops help to improve soil fertility by adding organic matter to the soil.
- Cover crops can help to control weeds by competing with them for water and nutrients.
- Cover crops are a key component of sustainable agriculture and can help to protect the health and productivity of our soils.
Examples
- A study by the USDA found that cover crops reduced soil erosion by an average of 50% on cornfields in the Midwest.
- A study by the University of Nebraska found that cover crops increased soil organic matter by an average of 10% on soybean fields in the Great Plains.
Challenges
- Cover crops can be difficult to establish on some soils.
- Cover crops can compete with cash crops for water and nutrients.
- Cover crops can harbor pests and diseases.
Conclusion
Cover crops are a valuable tool for farmers who want to reduce soil erosion, improve soil fertility, and control weeds. They are a key component of sustainable agriculture and can help to protect the health and productivity of our soils.
Windbreaks
Windbreaks are rows of trees or shrubs that are planted to reduce the force of the wind. They can be used to protect crops, livestock, and buildings from wind damage. Windbreaks can also help to reduce soil erosion by slowing down the wind and preventing it from blowing away topsoil.
- Reduced soil erosion: Windbreaks can reduce soil erosion by up to 50%. This is because the trees and shrubs in the windbreak act as a barrier to the wind, slowing it down and preventing it from blowing away topsoil.
- Improved crop yields: Windbreaks can also help to improve crop yields. This is because the windbreak reduces the force of the wind, which can damage crops. Windbreaks can also help to create a more favorable microclimate for crops, which can lead to increased yields.
- Reduced livestock losses: Windbreaks can also help to reduce livestock losses. This is because the windbreak provides shelter for livestock from the wind, which can help to prevent them from getting sick or injured.
- Reduced building damage: Windbreaks can also help to reduce building damage. This is because the windbreak reduces the force of the wind, which can prevent it from damaging buildings.
Windbreaks are a relatively simple and inexpensive practice that can be adopted by farmers of all sizes. They are a key component of sustainable agriculture and can help to protect the health and productivity of our soils.
Buffer strips
Buffer strips are areas of vegetation that are planted along the edges of fields, streams, and other water bodies. They help to reduce soil erosion, improve water quality, and provide wildlife habitat.
- Reduced soil erosion: Buffer strips help to reduce soil erosion by slowing down runoff and trapping sediment. This is important because soil erosion can lead to a loss of topsoil, nutrients, and organic matter, which can reduce crop yields and increase the risk of flooding and other environmental problems.
- Improved water quality: Buffer strips help to improve water quality by filtering pollutants from runoff. These pollutants can include sediment, nutrients, and pesticides. Buffer strips also help to slow down runoff, which gives the pollutants more time to settle out of the water.
- Wildlife habitat: Buffer strips provide habitat for a variety of wildlife species. These species include birds, mammals, reptiles, and amphibians. Buffer strips can also provide corridors for wildlife to move between different habitats.
Buffer strips are a relatively simple and inexpensive practice that can be adopted by farmers of all sizes. They are a key component of sustainable agriculture and can help to protect the health and productivity of our soils and water resources.
Grassed waterways
Grassed waterways are a farming practice that involves establishing a permanent vegetative cover in a natural or constructed channel to convey runoff from fields. They are an important component of soil erosion control and water quality protection. Grassed waterways reduce the velocity of runoff, allowing sediment to settle out and preventing it from being transported off-site. They also help to filter pollutants from runoff, such as nutrients and pesticides.
Grassed waterways are typically established in areas where runoff concentrates and causes erosion, such as at the bottom of slopes or in areas where runoff from multiple fields converges. They are typically seeded with a mixture of grasses and legumes that are adapted to the local climate and soil conditions.
Grassed waterways are an effective and relatively inexpensive way to reduce soil erosion and improve water quality. They are a key component of conservation farming systems and can help farmers to meet their environmental goals.
Key insights:
- Grassed waterways reduce soil erosion by slowing down runoff and allowing sediment to settle out.
- Grassed waterways improve water quality by filtering pollutants from runoff.
- Grassed waterways are a key component of conservation farming systems and can help farmers to meet their environmental goals.
Examples:
- A study by the USDA found that grassed waterways reduced soil erosion by an average of 50% on cornfields in the Midwest.
- A study by the University of Nebraska found that grassed waterways reduced sediment concentrations in runoff by an average of 75% on soybean fields in the Great Plains.
Challenges:
- Grassed waterways can be difficult to establish on some soils.
- Grassed waterways require regular maintenance to keep them functioning properly.
Contour buffer strips
Contour buffer strips are a farming practice that involves planting strips of vegetation along the contours of a slope. They are an effective way to reduce soil erosion and improve water quality. Contour buffer strips slow down runoff, allowing sediment to settle out and preventing it from being transported off-site. They also help to filter pollutants from runoff, such as nutrients and pesticides.
- Reduced soil erosion: Contour buffer strips reduce soil erosion by slowing down runoff and allowing sediment to settle out. This is important because soil erosion can lead to a loss of topsoil, nutrients, and organic matter, which can reduce crop yields and increase the risk of flooding and other environmental problems.
- Improved water quality: Contour buffer strips help to improve water quality by filtering pollutants from runoff. These pollutants can include sediment, nutrients, and pesticides. Contour buffer strips also help to slow down runoff, which gives the pollutants more time to settle out of the water.
- Wildlife habitat: Contour buffer strips provide habitat for a variety of wildlife species. These species include birds, mammals, reptiles, and amphibians. Contour buffer strips can also provide corridors for wildlife to move between different habitats.
- Reduced pesticide and fertilizer use: Contour buffer strips can help to reduce pesticide and fertilizer use. This is because the buffer strips help to filter pollutants from runoff, which reduces the amount of pesticides and fertilizers that are needed to protect crops.
Contour buffer strips are a key component of conservation farming systems. They are a relatively simple and inexpensive practice that can be adopted by farmers of all sizes. Contour buffer strips can help farmers to reduce soil erosion, improve water quality, and protect wildlife habitat.
No-till farming
No-till farming is a conservation farming practice that leaves crop residues on the field after harvest. This helps to reduce soil erosion by slowing down runoff and trapping sediment. No-till farming also helps to improve soil structure and water infiltration, and can reduce the need for pesticides and fertilizers.
- Reduced soil erosion: No-till farming can reduce soil erosion by up to 90%. This is because the crop residues left on the field act as a barrier to runoff, slowing it down and allowing sediment to settle out.
- Improved soil structure: No-till farming helps to improve soil structure by increasing the amount of organic matter in the soil. Organic matter helps to hold soil particles together and prevents them from being washed away by wind and water.
- Increased water infiltration: No-till farming also helps to increase water infiltration. This is because the crop residues left on the field help to slow down runoff and allow water to soak into the soil.
- Reduced need for pesticides and fertilizers: No-till farming can also help to reduce the need for pesticides and fertilizers. This is because the crop residues left on the field help to suppress weeds and pests, and they also help to release nutrients into the soil.
No-till farming is a sustainable farming practice that can help to reduce soil erosion, improve soil structure, increase water infiltration, and reduce the need for pesticides and fertilizers. It is a key component of conservation farming systems and can help farmers to meet their environmental goals.
FAQs About Farming Practices that Reduce Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is a serious problem that can lead to a loss of topsoil, nutrients, and organic matter, which can reduce crop yields and increase the risk of flooding and other environmental problems. Fortunately, there are a number of farming practices that can be used to reduce soil erosion.
Question 1: What are some of the most effective farming practices for reducing soil erosion?
Answer: Some of the most effective farming practices for reducing soil erosion include conservation tillage, contour farming, terracing, crop rotation, cover crops, windbreaks, buffer strips, grassed waterways, contour buffer strips, and no-till farming.
Question 2: How do these practices work to reduce soil erosion?
Answer: These practices work to reduce soil erosion by slowing down runoff and trapping sediment. They also help to improve soil structure and water infiltration, and can reduce the need for pesticides and fertilizers.
Question 3: What are the benefits of reducing soil erosion?
Answer: Reducing soil erosion has a number of benefits, including improved crop yields, reduced flooding, and improved water quality.
Question 4: What are some of the challenges associated with implementing these practices?
Answer: Some of the challenges associated with implementing these practices include the cost, the time required, and the need for specialized equipment.
Question 5: What can farmers do to overcome these challenges?
Answer: Farmers can overcome these challenges by working with government agencies and conservation organizations to find financial and technical assistance.
Question 6: What are some of the resources available to farmers who want to learn more about these practices?
Answer: There are a number of resources available to farmers who want to learn more about these practices, including government websites, university extension services, and conservation organizations.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought:
Soil erosion is a serious problem, but it can be reduced by using a variety of farming practices. These practices have a number of benefits, including improved crop yields, reduced flooding, and improved water quality. Farmers who are interested in implementing these practices can find a number of resources to help them get started.
Transition to the next article section:
For more information on farming practices that reduce soil erosion, please see the following resources:
- Website of the Natural Resources Conservation Service
- Website of the Soil and Water Conservation Society
- Website of the American Farmland Trust
Tips to Reduce Soil Erosion
Soil erosion is a serious problem that can lead to a loss of topsoil, nutrients, and organic matter, which can reduce crop yields and increase the risk of flooding and other environmental problems. Fortunately, there are a number of farming practices that can be used to reduce soil erosion.
Tip 1: Use conservation tillage.
Conservation tillage leaves crop residues on the field after harvest, which helps to slow down runoff and trap sediment. This practice can reduce soil erosion by up to 90%.
Tip 2: Implement contour farming.
Contour farming involves planting crops in rows that follow the contours of the land, which helps to reduce runoff and erosion. This practice can reduce soil erosion by up to 50%.
Tip 3: Terrace sloping land.
Terracing involves building terraces on sloping land to slow down runoff and trap sediment. This practice can reduce soil erosion by up to 90%.
Tip 4: Practice crop rotation.
Crop rotation involves growing different crops on the same land in a sequential order, which helps to reduce soil erosion, improve soil fertility, and control pests and diseases.
Tip 5: Plant cover crops.
Cover crops are a farming practice that involves growing a crop of plants on land that would otherwise be left fallow. Cover crops help to reduce soil erosion, improve soil fertility, and control weeds.
Tip 6: Establish windbreaks.
Windbreaks are rows of trees or shrubs that are planted to reduce the force of the wind. Windbreaks can help to reduce soil erosion by up to 50%. They can also improve crop yields, reduce livestock losses, and reduce building damage.
Tip 7: Create buffer strips.
Buffer strips are areas of vegetation that are planted along the edges of fields, streams, and other water bodies. Buffer strips help to reduce soil erosion, improve water quality, and provide wildlife habitat.
Tip 8: Install grassed waterways.
Grassed waterways are a farming practice that involves establishing a permanent vegetative cover in a natural or constructed channel to convey runoff from fields. Grassed waterways reduce the velocity of runoff, allowing sediment to settle out and preventing it from being transported off-site. They also help to filter pollutants from runoff, such as nutrients and pesticides.
Summary of key takeaways or benefits:
By using these and other farming practices, farmers can help to reduce soil erosion and protect the health and productivity of their soils.
Transition to the article’s conclusion:
Soil erosion is a serious problem, but it can be reduced by using a variety of farming practices. These practices have a number of benefits, including improved crop yields, reduced flooding, and improved water quality. Farmers who are interested in implementing these practices can find a number of resources to help them get started.
Conclusion
Soil erosion is a serious problem that can lead to a loss of topsoil, nutrients, and organic matter, which can reduce crop yields and increase the risk of flooding and other environmental problems. However, there are a number of farming practices that can be used to reduce soil erosion, including conservation tillage, contour farming, terracing, crop rotation, cover crops, windbreaks, buffer strips, grassed waterways, contour buffer strips, and no-till farming.
These practices work by slowing down runoff and trapping sediment, which helps to protect the soil from erosion. They also help to improve soil structure and water infiltration, and can reduce the need for pesticides and fertilizers. By using these and other farming practices, farmers can help to reduce soil erosion and protect the health and productivity of their soils.