Table of Contents
Farming practices in Canada contribute significantly to the country’s economy and food security.
Editor’s Note: This guide explores farming practices in Canada, highlighting their importance and the benefits they offer.
Through extensive research and analysis, we have compiled this comprehensive guide to assist readers in understanding the nuances of farming practices in Canada.
Key Differences:
| Characteristic | Conventional Farming | Sustainable Farming |
|---|---|---|
| Methods | Relies heavily on synthetic fertilizers and pesticides | Emphasizes natural methods, such as crop rotation and organic fertilizers |
| Environmental Impact | Can contribute to soil degradation and water pollution | Minimizes environmental impact and promotes biodiversity |
| Economic Considerations | Higher input costs due to reliance on chemicals | Lower input costs and potential for premium pricing for sustainably produced crops |
Main Article Topics:
- History and Evolution of Farming Practices in Canada
- Current Trends in Canadian Agriculture
- Challenges and Opportunities for Canadian Farmers
- The Role of Technology in Modern Farming
- The Future of Farming in Canada
Farming Practices in Canada
Farming practices in Canada are diverse and complex, reflecting the country’s vast geography, climate, and agricultural history.
- Sustainable
- Technology-driven
- Export-oriented
- Diverse
- Challenging
- Government-supported
- Research-intensive
- Environmentally conscious
- Adaptable
These aspects are interconnected and shape the way that farming is practiced in Canada. For example, the country’s vast geography and diverse climate require farmers to adopt adaptable practices that can withstand extreme weather conditions and different soil types. The government’s support for agriculture, through policies and funding, helps to create a stable environment for farmers and encourages sustainable practices. Research and technology are also essential for Canadian farmers, as they strive to improve yields, reduce costs, and minimize their environmental impact.
Overall, the key aspects of farming practices in Canada reflect the country’s commitment to sustainable, efficient, and globally competitive agriculture.
Sustainable
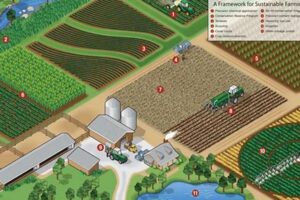
Sustainability is a key aspect of farming practices in Canada. Canadian farmers are committed to protecting the environment and ensuring the long-term viability of their operations. This includes adopting practices that conserve soil, water, and biodiversity.
- Environmental stewardship: Canadian farmers are committed to protecting the environment. They use practices such as crop rotation, cover cropping, and integrated pest management to minimize their environmental impact.
- Water conservation: Water is a precious resource, and Canadian farmers are working to conserve it. They use irrigation systems that are efficient and minimize water waste.
- Soil health: Soil is the foundation of agriculture, and Canadian farmers are working to protect and improve soil health. They use practices such as no-till farming and cover cropping to build soil organic matter and reduce erosion.
- Biodiversity: Canadian farmers are working to promote biodiversity on their farms. They plant a variety of crops and provide habitat for wildlife.
Sustainable farming practices are essential for the long-term viability of agriculture in Canada. By protecting the environment, conserving resources, and promoting biodiversity, Canadian farmers are ensuring that they can continue to produce food for a growing population in a sustainable way.
Technology-driven
Technology is playing an increasingly important role in farming practices in Canada. Farmers are using technology to improve efficiency, productivity, and sustainability.
- Precision agriculture: Precision agriculture is a farming management concept that uses information technology to ensure that crops and soil receive exactly what they need for optimal health and productivity. This can involve using GPS, sensors, and data analytics to monitor crop health, soil conditions, and weather patterns.
- Automated machinery: Automated machinery is another important aspect of technology-driven farming. Farmers are using automated tractors, planters, and harvesters to reduce labor costs and improve efficiency.
- Data analysis: Farmers are also using data analysis to make better decisions about their operations. They can use data to track crop yields, identify trends, and predict future performance.
- E-commerce: E-commerce is also playing a role in technology-driven farming. Farmers are using online platforms to sell their products directly to consumers.
Technology is having a major impact on farming practices in Canada. Farmers are using technology to improve efficiency, productivity, and sustainability. This is helping to ensure that Canada remains a leading agricultural producer.
Export-oriented
Canada is a major exporter of agricultural products, and this has a significant impact on farming practices in the country. In order to meet the demands of the global market, Canadian farmers must produce high-quality, safe, and affordable food. This requires them to adopt efficient and sustainable farming practices.
For example, Canadian farmers are using precision agriculture technologies to improve their yields and reduce their environmental impact. They are also working to develop new and innovative products that meet the needs of consumers around the world.
The export orientation of Canadian agriculture has a number of benefits for the country. It helps to create jobs, boost the economy, and support rural communities. It also gives Canadian farmers access to a wider market for their products.
However, there are also some challenges associated with export-oriented agriculture. For example, Canadian farmers are subject to the vagaries of the global market, and they must be able to compete with farmers from other countries. Additionally, export-oriented agriculture can lead to environmental problems, such as soil erosion and water pollution.
Overall, the export orientation of Canadian agriculture is a complex issue with both benefits and challenges. Canadian farmers must be able to adapt to the changing demands of the global market while also protecting the environment and ensuring the sustainability of their operations.
Key insights:
- Export-oriented agriculture is a major driver of farming practices in Canada.
- Canadian farmers must adopt efficient and sustainable farming practices in order to meet the demands of the global market.
- The export orientation of Canadian agriculture has a number of benefits for the country, including job creation, economic growth, and support for rural communities.
- There are also some challenges associated with export-oriented agriculture, such as exposure to the global market and environmental problems.
- Canadian farmers must be able to adapt to the changing demands of the global market while also protecting the environment and ensuring the sustainability of their operations.
Diverse
Farming practices in Canada are diverse due to the country’s vast geography, climate, and agricultural history. This diversity is reflected in the wide range of crops and livestock that are produced in Canada, as well as the different farming systems that are used.
The diversity of farming practices in Canada is important for a number of reasons. First, it allows farmers to adapt to the different environmental conditions that exist across the country. For example, farmers in the Prairies grow wheat and other grains, while farmers in British Columbia grow fruits and vegetables. Second, the diversity of farming practices helps to reduce the risk of crop failure. If one crop fails, farmers can often switch to another crop that is better suited to the conditions.
The following table provides a few examples of the diverse farming practices that are used in Canada:
| Region | Farming System | Crops | Livestock |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prairies | Grain farming | Wheat, barley, canola | Cattle, hogs |
| Ontario | Mixed farming | Corn, soybeans, wheat, hay | Cattle, hogs, poultry |
| Quebec | Dairy farming | Corn, soybeans, hay | Dairy cattle |
| British Columbia | Fruit and vegetable farming | Apples, pears, cherries, vegetables | Cattle, poultry |
The diversity of farming practices in Canada is a strength for the country’s agricultural sector. It allows farmers to adapt to different environmental conditions, reduce the risk of crop failure, and produce a wide range of food products.
Challenging
Farming practices in Canada are influenced by a variety of challenges, including:
- Climate change: Climate change is a major challenge for farmers in Canada. The country is experiencing more extreme weather events, such as droughts, floods, and heat waves. These events can damage crops and livestock, and make it difficult for farmers to plan for the future.
- Pests and diseases: Pests and diseases are a constant threat to crops and livestock. Farmers must use a variety of methods to control pests and diseases, which can be expensive and time-consuming.
- Market volatility: The prices of agricultural products can fluctuate dramatically, which can make it difficult for farmers to plan their operations. Farmers must be able to adapt to changing market conditions in order to remain profitable.
- Labor shortages: There is a shortage of skilled labor in the agricultural sector. This can make it difficult for farmers to find the workers they need to operate their farms.
These challenges can make it difficult for farmers in Canada to succeed. However, there are a number of programs and resources available to help farmers overcome these challenges. Farmers can also adopt a variety of strategies to mitigate the risks associated with these challenges.
Government-supported
Government support plays a significant role in shaping farming practices in Canada. The government provides financial assistance, research, and regulations to support farmers and the agricultural sector.
- Financial assistance: The government provides financial assistance to farmers through a variety of programs, such as crop insurance, disaster relief, and farm loans. This assistance helps farmers to manage risk and invest in their operations.
- Research: The government supports agricultural research through funding and partnerships with universities and research institutions. This research helps to develop new technologies and practices that can improve farm productivity and sustainability.
- Regulations: The government also regulates the agricultural sector to protect consumers and the environment. These regulations cover areas such as food safety, animal welfare, and pesticide use.
Government support helps to create a stable and sustainable environment for farming in Canada. It provides farmers with the resources they need to succeed and helps to ensure that Canadian agriculture remains competitive in the global marketplace.
Research-intensive
Farming practices in Canada are research-intensive, meaning that farmers rely heavily on research to improve their productivity and sustainability. This research is conducted by universities, government agencies, and private companies. It covers a wide range of topics, including crop production, livestock management, and environmental protection.
Research has played a major role in the development of Canadian agriculture. For example, research has led to the development of new crop varieties that are more resistant to pests and diseases, more tolerant of drought and heat, and more productive.
Research is also essential for the development of sustainable farming practices. For example, research has led to the development of new technologies that can help farmers to reduce their use of pesticides and fertilizers, and to improve their water and soil conservation practices.
The following table provides a few examples of the practical benefits of research-intensive farming practices in Canada:
| Research Area | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Crop production | Increased yields, improved quality |
| Livestock management | Improved animal health and welfare, increased productivity |
| Environmental protection | Reduced pesticide and fertilizer use, improved water and soil conservation |
Research-intensive farming practices are essential for the sustainability and competitiveness of Canadian agriculture. By investing in research, farmers can improve their productivity, reduce their environmental impact, and meet the demands of the global marketplace.
Environmentally conscious
Environmental consciousness is a key aspect of farming practices in Canada. Farmers are increasingly adopting practices that protect the environment and promote sustainability. This is driven by a number of factors, including consumer demand for environmentally friendly products, government regulations, and a growing awareness of the importance of environmental stewardship.
- Sustainable land management: Canadian farmers are using sustainable land management practices to protect the soil and water resources. These practices include crop rotation, cover cropping, and reduced tillage.
- Water conservation: Farmers are also implementing water conservation practices, such as irrigation scheduling and drip irrigation, to reduce their water use.
- Integrated pest management (IPM): IPM is a holistic approach to pest control that emphasizes prevention and natural methods. Farmers are using IPM to reduce their reliance on pesticides.
- Precision agriculture: Precision agriculture is a farming management concept that uses information technology to ensure that crops and soil receive exactly what they need for optimal health and productivity. This can help farmers to reduce their environmental impact by reducing their use of fertilizers and pesticides.
By adopting environmentally conscious farming practices, Canadian farmers are helping to protect the environment and ensure the sustainability of agriculture in the country.
Adaptable
Farming practices in Canada must be adaptable to changing conditions, including climate change, market volatility, and new technologies. Canadian farmers have a long history of adapting their practices to meet the challenges of their environment and the demands of the marketplace.
For example, in recent years, Canadian farmers have adopted precision agriculture technologies to improve their yields and reduce their environmental impact. They have also developed new crop varieties that are more resistant to pests and diseases and more tolerant of drought and heat.
The ability to adapt is essential for the sustainability of farming in Canada. By adopting new technologies and practices, Canadian farmers can continue to produce high-quality food for a growing population, while also protecting the environment and ensuring the long-term viability of their operations.
Here are some specific examples of how Canadian farmers are adapting their practices to meet the challenges of the 21st century:
| Challenge | Adaptation |
|---|---|
| Climate change | Developing new crop varieties that are more resistant to pests, diseases, drought, and heat; adopting irrigation technologies to cope with water shortages; using cover crops to improve soil health and reduce erosion. |
| Market volatility | Diversifying crops and livestock; developing new markets for value-added products; using marketing cooperatives to pool resources and negotiate better prices. |
| New technologies | Adopting precision agriculture technologies to improve yields and reduce environmental impact; using drones to monitor crops and livestock; using data analysis to make better decisions about farm management. |
By adapting their practices to meet the challenges of the 21st century, Canadian farmers are ensuring the sustainability of agriculture in Canada and continuing to produce high-quality food for a growing population.
FAQs about Farming Practices in Canada
This section addresses frequently asked questions to provide a comprehensive understanding of farming practices in Canada.
Question 1: What are the key aspects of farming practices in Canada?
Farming practices in Canada are diverse, technology-driven, export-oriented, sustainable, challenging, government-supported, adaptable, research-intensive, and environmentally conscious. These aspects shape the way farming is practiced in Canada, ensuring the production of high-quality food while protecting the environment.
Question 2: How are farming practices in Canada adapting to climate change?
Canadian farmers are adopting various strategies to adapt to climate change. These include developing new crop varieties that are more resistant to pests, diseases, drought, and heat; adopting irrigation technologies to cope with water shortages; and using cover crops to improve soil health and reduce erosion.
Question 3: What role does technology play in farming practices in Canada?
Technology plays a crucial role in Canadian agriculture. Farmers are using precision agriculture technologies to improve yields and reduce environmental impact, drones to monitor crops and livestock, and data analysis to make informed decisions about farm management.
Question 4: How are Canadian farmers addressing market volatility?
To address market volatility, Canadian farmers are diversifying crops and livestock, developing new markets for value-added products, and using marketing cooperatives to pool resources and negotiate better prices.
Question 5: What are the environmental considerations in Canadian farming practices?
Canadian farmers are committed to environmental sustainability. They use sustainable land management practices, implement water conservation measures, adopt integrated pest management, and utilize precision agriculture to reduce their environmental impact.
Question 6: How does government support contribute to farming practices in Canada?
Government support plays a significant role in shaping farming practices in Canada. The government provides financial assistance, research, and regulations to support farmers and ensure a stable and sustainable agricultural sector.
These FAQs provide a comprehensive overview of key aspects, challenges, and adaptations in farming practices in Canada. By embracing innovation, sustainability, and government support, Canadian farmers continue to produce high-quality food while navigating the evolving agricultural landscape.
Next, we will explore the importance of sustainable farming practices in Canada and their impact on the environment and the economy.
Tips for Sustainable Farming Practices in Canada
Sustainable farming practices are essential for the long-term viability of agriculture in Canada. By adopting sustainable practices, farmers can protect the environment, conserve resources, and improve profitability.
Tip 1: Implement crop rotation. Crop rotation is the practice of growing different crops on the same land in a sequential order. This helps to improve soil health, reduce erosion, and control pests and diseases.
Tip 2: Use cover crops. Cover crops are plants that are grown to cover the soil during the off-season. This helps to protect the soil from erosion, improve soil structure, and add nutrients to the soil.
Tip 3: Reduce tillage. Tillage is the practice of turning over the soil. However, excessive tillage can damage soil structure and lead to erosion. By reducing tillage, farmers can protect the soil and improve its health.
Tip 4: Use integrated pest management (IPM). IPM is a holistic approach to pest control that emphasizes prevention and natural methods. By using IPM, farmers can reduce their reliance on pesticides and protect the environment.
Tip 5: Adopt precision agriculture technologies. Precision agriculture technologies use data to help farmers make more informed decisions about their operations. This can help farmers to reduce their environmental impact and improve their yields.
Tip 6: Manage water resources efficiently. Water is a precious resource, and farmers need to use it wisely. By implementing water conservation measures, farmers can reduce their water use and protect water quality.
Tip 7: Protect biodiversity. Biodiversity is essential for the health of agricultural ecosystems. By planting a variety of crops and providing habitat for wildlife, farmers can help to protect biodiversity.
Tip 8: Seek professional advice. There are many resources available to help farmers adopt sustainable practices. Farmers should seek advice from agricultural professionals, such as extension agents and crop consultants, to develop a sustainable farming plan.
By adopting sustainable farming practices, Canadian farmers can protect the environment, conserve resources, and improve profitability. Sustainable farming is the key to the long-term viability of agriculture in Canada.
Farming Practices in Canada
Farming practices in Canada are diverse, reflecting the country’s vast geography, climate, and agricultural history. Canadian farmers are committed to producing high-quality food while protecting the environment and ensuring the sustainability of their operations. This is achieved through the adoption of sustainable practices, the use of technology, and the support of government policies.
The future of farming in Canada is bright. The country has a strong agricultural sector, and farmers are continually adopting new technologies and practices to improve their productivity and sustainability. Canadian farmers are also well-positioned to meet the growing global demand for food. By continuing to invest in research and innovation, and by working together with governments and other stakeholders, Canadian farmers can ensure that the country remains a leader in sustainable agriculture.